In this guide, we will examine all the features and characteristics of PBoC’s proposed digital currency. As we go over facts, we will determine the impact of Digital RMB on the price of the Yuan, China’s economy and the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Why Digital RMB?
At a first glance, Digital RMB is China’s attempt at a comeback for Yuan’s demand and prices among local and international investors. Increasing tension in the US-China trade war led to a loss of investors’ faith in the Yuan and this was followed by a massive sell-off in China. PBoC had accelerated plans of Digital RMB’s launch right after Facebook’s announcement of Libra’s launch. However, growing concerns in Beijing led to continuous capital outflow and weakened RMB further. Most investors divested from Yuan to Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. This triggered a series of events that inspired PBoC to work on Digital RMB’s launch and bring it in the market as soon as possible.
Two-tiered prototype
The Digital RMB will be backed by 1:1 fiat reserves (M0 supply) which will help in managing anonymity and encryption. Based on recent details shared by PBoC, their digital currency would be based on a “two-tier system” for issuance and redemption. The first layer would be for issuance and distribution of RMB to commercial banks and the second would be for re-distribution to retail investors. However, it remains unclear how blockchain technology would be implemented in the second layer as PBoC has shared no clear roadmap for the currency. Reports state that China plans to design the currency in a way that transfers between entities would not require a bank account.
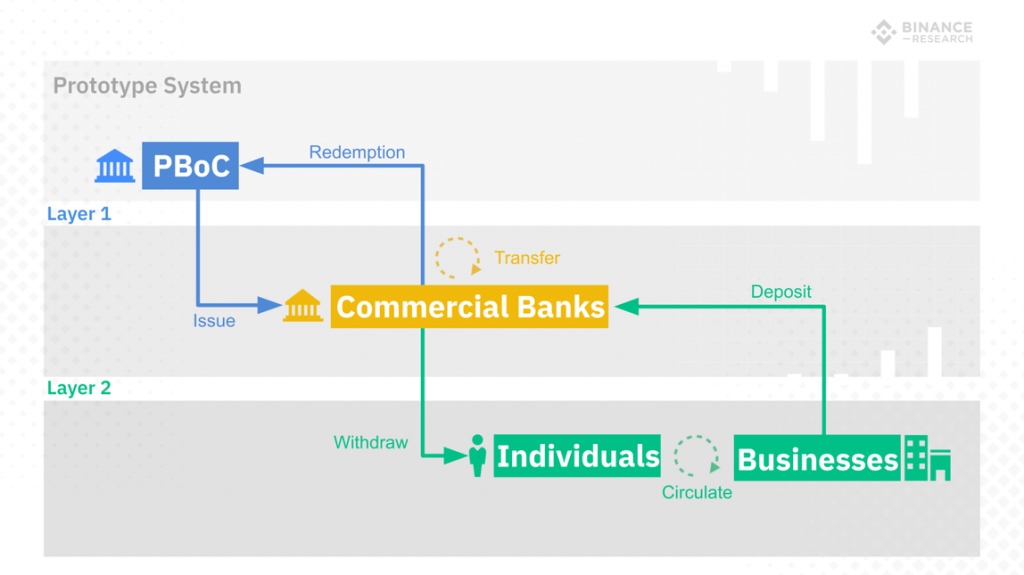
Image Courtesy: Binance Research
Tier 1: Issuance and Distribution
To maintain monetary sovereignty, the digital RMB will be issued solely by the PBoC. This will ensure that the currency is legal tender and the bank will have complete control over its supply and circulation. The first tier involves the distribution of the currency to commercial banks. While Facebook’s Libra will directly be distributed to retail investors and governed by an overseas entity, digital RMB will be distributed in two tiers and controlled by the Central Bank.
Tier 1 institutions include five commercial banks: China Construction Bank, the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, the Bank of China and the Agricultural Bank of China. Other partners would include Union Pay (Chinese banking association) and online payment service providers like Alibaba and Tencent.
Tier 2: Re-distribution to retail investors
Commercial banks and other payment partners would redistribute tokens to the general public, businesses, and entities. The process of deposit and withdrawal will be the same as domestic commercial banks. This will eliminate the need for paper money without altering the existing monetary issuance and circulation system.
Where will it be used?
- Retail Payments: It will ensure anonymity and ease of use for making retail payments
- Outward remittance: The currency will lower the cost of outward remittance and increase the speed of transactions. This move will ultimately promote the internationalization of digital RMB
- Existing cash-based systems: PBoC intends to replace cash with digital RMB and reduce the operation and maintenance costs of paper money
Earning interest on Digital RMB
If users park their Digital RMB in financial institutions, they will receive interest from PBoC. No interest is to be earned if the currency is held outside of the financial institutions. This feature ensures that the currency does not compete with existing deposits and schemes for earning interest.
Anonymity in P2P transactions
Digital RMB contains a user id and owner information for each transaction. Each time a new transaction is generated, a new CBDC string is created, and it contains the new owner’s identity. Though transactions are anonymous at the user level, it is possible to retrieve the entire log of user transactions and this makes Digital RMB fungible. Unlike altcoins like Ethereum and Monero, in Digital RMB, the centralized authority (PBoC) will be able to gather information and maintain logs for all transactions. User identity will be tied to individual wallets and this will make it completely anonymous.
PBoC aims to improve the effectiveness and control of its monetary policy through Digital RMB. Beijing will map out an even more detailed picture of individuals and entities across China and increase RMB’s turnover until it hits internationalization. There are certain risks associated with anonymity and abuse of individual financial privacy, however, the bank plans to eliminate these in later stages of Digital RMB’s development.
Disclaimer
Content provided by CryptoTraderNews is for informational purposes only, and should not be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice. All information is of a general nature. As always, there is risk with any investment. In exchange for using our products and services, you agree not to hold CryptoTraderNews Pro, its affiliates, or any third party service provider liable for any possible claim for damages arising from decisions you make based on information made available to you through our services.

1 comment
[…] People’s Bank of China’s announcement of launching Digital RMB after Facebook’s announcement of Libra’s launch indicates that cryptocurrencies are more […]
Comments are closed.